Hose Crimper: Hydraulic, Manual & Electric Options For Sale
Introduction to Advanced Hose Crimping Technologies
In industrial operations, the integrity and reliability of fluid transfer systems are paramount. At the heart of ensuring leak-free, high-performance connections for hydraulic and industrial hoses lies the hose crimper. This indispensable piece of equipment mechanically compresses a fitting onto a hose, creating a secure and durable assembly capable of withstanding extreme pressures, temperatures, and dynamic stresses. The evolution of crimping technology has transitioned from basic manual tools to sophisticated automated systems, meeting the rigorous demands of modern industries for precision, efficiency, and safety. This article delves into the critical aspects of modern hose crimping, including manufacturing processes, industry trends, technical specifications, diverse application scenarios, and key advantages that contribute to operational excellence.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of performance and reliability, understanding the intricacies of hose crimping becomes crucial for B2B decision-makers and technical professionals. From the robust construction of the crimping dies to the intelligent control systems that ensure consistent results, every component plays a vital role in the overall system's integrity. We will explore how manufacturers are addressing these challenges through innovative designs, material science, and stringent quality control, ultimately leading to superior hose assemblies that enhance safety and operational longevity.
The Manufacturing Process of a High-Performance Hose Crimper
The production of a robust and precise hose crimper is a meticulous process, demanding high-quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques. The aim is to achieve unparalleled durability, consistent performance, and exceptional accuracy for critical industrial applications. The core components, such as the crimping head, dies, and hydraulic cylinder, are engineered to withstand immense forces and repetitive cycles.
Materials and Fabrication:
- Main Frame & Body: Typically constructed from high-strength steel alloys, often through processes like precision welding of heavy-gauge steel plates or robust ductile iron casting. These materials ensure structural integrity and resistance to deformation under extreme crimping forces.
- Crimping Dies: Critical for accuracy and longevity, dies are usually forged from premium tool steels (e.g., D2, H13) known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. After forging, they undergo precise CNC machining to achieve exact tolerances, followed by specialized heat treatment processes (e.g., nitriding, induction hardening) to optimize surface hardness and core strength.
- Hydraulic Components: Cylinders, pistons, and pumps are fabricated from high-grade alloy steels and precision ground to ensure smooth operation, minimal friction, and leak-free performance. Seals are selected from materials compatible with various hydraulic fluids and designed for long service life.
Manufacturing Process Flow:
- Design & Engineering: Utilizing advanced CAD/CAM software to design components, perform finite element analysis (FEA) for stress testing, and optimize ergonomics and functionality.
- Material Sourcing: Selection and procurement of certified raw materials that meet strict metallurgical specifications.
- Initial Fabrication: Forging, casting, or cutting of primary components like the machine frame, die segments, and hydraulic cylinder bodies.
- Precision Machining: Extensive use of multi-axis CNC machining centers for milling, turning, grinding, and drilling to achieve micron-level tolerances, especially for die bores and piston surfaces.
- Heat Treatment: Application of specific heat treatment protocols (e.g., carburizing, quenching, tempering) to enhance the hardness, strength, and wear resistance of critical components, particularly the crimping dies.
- Surface Finishing: Processes like grinding, polishing, and often surface coatings (e.g., hard chrome plating, black oxide) are applied to reduce friction, improve corrosion resistance, and extend component life.
- Assembly: Skilled technicians assemble the mechanical, hydraulic, and electrical systems, ensuring proper alignment, torque specifications, and system integration.
- Quality Control & Testing: Each hose crimper undergoes rigorous testing protocols, including hydrostatic pressure testing for hydraulic systems, dimensional accuracy checks for die closure, cycle life testing, and functional performance assessments.
Testing Standards and Service Life:
Manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Performance testing often aligns with industry-specific standards like ANSI B30.1 for hydraulic jacks or CE certification for European market compliance. A well-maintained hose crimper, built to these standards, typically offers a service life exceeding 10-15 years, even under demanding industrial conditions.
Target Industries and Advantages:
These machines are critical across a spectrum of industries, including petrochemical, metallurgy, mining, construction, water supply & drainage, agriculture, and automotive manufacturing. In these sectors, the advantages are profound:
- Energy Saving: Modern hydraulic systems in electric crimpers are designed for efficiency, minimizing power consumption through optimized pump designs and motor controls.
- Corrosion Resistance: Components exposed to harsh environments often feature specialized coatings or stainless steel construction, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.
- Precision & Consistency: Advanced control systems guarantee precise crimping diameters, reducing human error and ensuring uniform, high-quality hose assemblies.
- Enhanced Safety: Reliable crimps minimize the risk of hose bursts and fluid leaks, significantly improving workplace safety.
Industry Trends in Hose Crimping Technology
The hose crimping industry is continually evolving, driven by demands for increased efficiency, safety, and technological integration. Several key trends are shaping the future of hose crimper design and application:
- Automation and Digitalization: The shift towards fully automated crimping machines is accelerating. These systems often feature touch-screen interfaces, digital control over crimp diameter and force, and integration with production management software. This reduces manual labor, minimizes errors, and enhances consistency.
- IoT and Predictive Maintenance: Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) allows for real-time monitoring of machine performance, predictive maintenance scheduling, and remote diagnostics. This reduces downtime and optimizes operational efficiency.
- Portability and Versatility: While large industrial machines remain crucial, there's a growing demand for compact, portable crimpers, especially for field service and on-site repairs. Innovations in manual hose crimper and hyd hose crimper designs focus on lightweight materials and efficient power sources to facilitate mobility without sacrificing crimping power.
- Higher Pressure and Larger Diameter Capabilities: As industrial systems operate at increasingly higher pressures, crimpers must be capable of handling larger diameter hoses with increased wall thickness and reinforcement. This requires stronger machine frames, more powerful hydraulics, and specialized die designs.
- Environmental and Safety Compliance: Emphasis on reduced noise levels, energy-efficient operations, and improved safety features (e.g., emergency stops, safety guards, auto-retract functions) is becoming standard. The use of biodegradable hydraulic fluids is also gaining traction.
- Smart Crimping: Advanced sensors and algorithms are being developed to measure crimp force and diameter in real-time, providing feedback to ensure crimps meet exact specifications and preventing under- or over-crimping. This ensures optimal performance and safety, especially with complex multi-spiral hoses.
Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
Understanding the technical specifications of a hose crimper is crucial for selecting the right equipment for specific industrial applications. Key parameters define a machine's capability, precision, and operational efficiency.
Typical Hose Crimper Specifications:
| Parameter | Value Range | Description / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Crimping Force | 150 - 600+ Tons | Maximum force applied to the dies. Higher force for larger diameter, multi-spiral, or stiffer hoses. Critical for secure crimps on hyd hose crimper applications. |
| Hose ID Capacity | 1/4" - 6" (6mm - 150mm) | Range of internal hose diameters the machine can crimp. Dictates versatility. |
| Max Die Opening | 50 - 200 mm | The maximum gap between dies. Important for accommodating large fittings and elbow connectors. |
| Motor Power (Electric) | 2.2 - 11 kW (3 - 15 HP) | For electric hose crimper models, determines crimping speed and continuous duty capability. |
| System Voltage | 230V / 400V / 480V (3-phase) | Electrical requirements, critical for facility integration. |
| Crimping Accuracy | ±0.1mm - ±0.05mm | Precision of the final crimp diameter, crucial for sealing and burst pressure resistance. Achieved through micro-adjustment systems. |
| Cycle Time | 6 - 20 seconds (no load) | Time taken for one full crimp cycle (close and open). Impacts production throughput. |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | Variable (e.g., 700x600x1300mm) | Physical footprint of the machine, important for workshop layout. |
| Weight | 150 - 1500 kg | Overall mass, influencing portability (for smaller units) and stability (for larger units). |
Diverse Application Scenarios of Hose Crimpers
The versatility of the hose crimper makes it indispensable across a vast array of industries, each with unique demands for fluid power transmission and material transfer. From heavy industrial machinery to delicate control systems, precise hose assemblies are critical for operational safety and efficiency.
- Construction and Heavy Machinery: Hydraulic systems power excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and loaders. These machines operate under high pressure and intense vibrations, requiring robust hose assemblies to prevent leaks and catastrophic failures. A reliable hyd hose crimper ensures these critical connections remain secure, minimizing downtime on construction sites.
- Agriculture: Tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems rely heavily on hydraulic and pneumatic hoses. Crimpers ensure reliable connections for steering, lifting, and power take-off functions, crucial for efficient farming operations. The ability to perform on-site repairs with a portable unit like a manual hose crimper can be a significant advantage.
- Mining: In harsh mining environments, hoses are subjected to abrasive materials, extreme temperatures, and high pressures. Durable crimped hoses are essential for hydraulic shovels, roof supports, and waterjet cutting equipment, directly impacting miner safety and productivity.
- Oil & Gas Exploration and Production: From drilling rigs to refineries, hoses transport various fluids, often under very high pressure and corrosive conditions. Precisely crimped hoses are vital for maintaining system integrity, preventing costly spills, and ensuring safe operations in volatile environments.
- Transportation (Automotive & Marine): In the automotive sector, crimpers are used for brake lines, air conditioning hoses, and power steering lines. In marine applications, they ensure robust fluid transfer systems on vessels, from small boats to large cargo ships, where reliability in saltwater environments is critical.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Plants: Factories utilize hydraulic and pneumatic power for automated machinery, presses, and assembly lines. Reliable hose crimps prevent production delays, maintain consistent performance, and enhance the safety of workers operating heavy equipment.
- Waste Management: Refuse trucks and compactors use powerful hydraulic systems. The constant stresses of lifting, compressing, and ejecting waste require exceptionally strong and reliable hose connections.
In all these scenarios, the primary advantage of a precisely crimped hose assembly is the creation of a leak-proof connection that can withstand the specified operating pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions. This directly translates to enhanced operational safety, reduced maintenance costs, and increased equipment longevity.
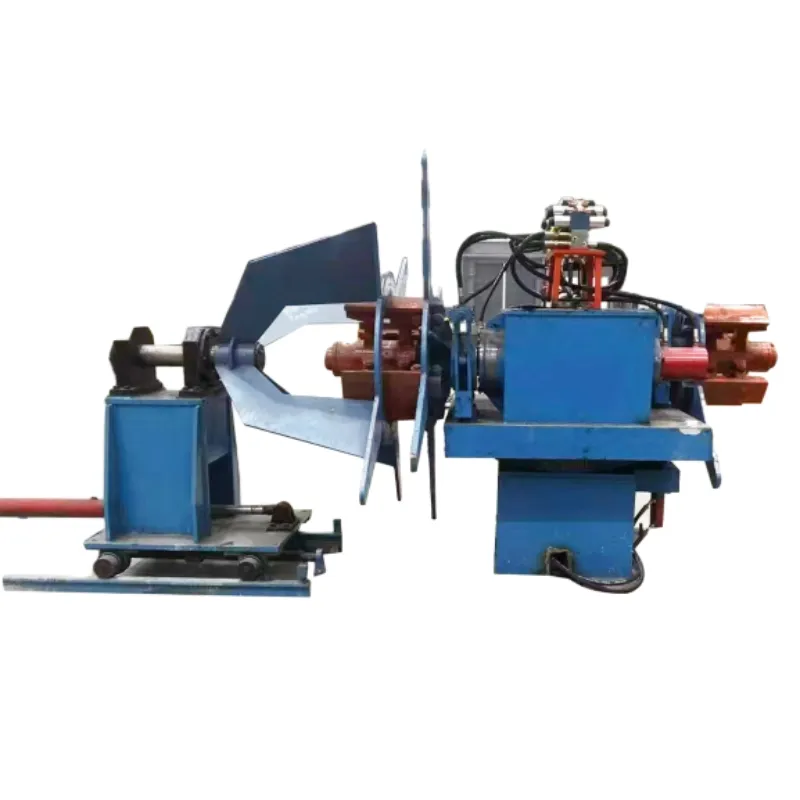

Technical Advantages of Modern Hose Crimpers
Modern hose crimper technologies offer significant technical advantages that elevate the quality, reliability, and efficiency of hose assembly operations. These advancements are crucial for industries where performance is non-negotiable.
- Unmatched Precision and Repeatability: Advanced crimpers feature digital control systems that allow for precise diameter settings, often with micro-adjustments as fine as 0.01mm. This ensures consistent crimp specifications across multiple assemblies, critical for standardized production and avoiding deviations that could lead to failures.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Modern machines incorporate safety mechanisms such as emergency stop buttons, interlocked safety guards, and automatic pressure relief valves. These features protect operators and prevent damage to the equipment during operation.
- Reduced Downtime and Increased Productivity: Features like quick-change die systems and intuitive user interfaces streamline the crimping process, significantly reducing setup times and increasing throughput. Automated or semi-automated cycles improve efficiency compared to older manual hose crimper models.
- Versatility Across Hose Types and Sizes: With a wide range of interchangeable dies and adjustable settings, a single modern crimper can handle various hose types (e.g., textile braid, wire braid, multi-spiral) and materials (rubber, thermoplastic), along with a broad spectrum of diameters and fitting styles.
- Robust Construction and Durability: Engineered with high-grade materials and precision manufacturing, these machines are built to withstand continuous, heavy-duty operation in demanding industrial environments, ensuring a long operational life and low total cost of ownership.
- Diagnostic and Data Logging Capabilities: Many electric hose crimper and hyd hose crimper models offer integrated diagnostic systems that monitor machine health and log operational data. This data is invaluable for quality assurance, troubleshooting, and predictive maintenance.
- Optimized Energy Consumption: Modern hydraulic power units are designed for energy efficiency, utilizing variable frequency drives (VFDs) and intelligent pump controls to consume power only when needed, leading to reduced operational costs.
These technical advantages collectively contribute to higher quality hose assemblies, improved operational safety, and greater economic returns for businesses relying on fluid power systems.
Vendor Comparison: Selecting the Right Hose Crimper
Choosing the appropriate hose crimper involves a thorough evaluation of various vendors and their offerings. Key factors like crimping force, hose capacity, automation, and after-sales support differentiate products available for sale. Below is a comparative overview of hypothetical vendor offerings, illustrating critical decision-making parameters for a hose crimper for sale.
| Feature | Vendor A (Premium) | Vendor B (Mid-Range) | Vendor C (Entry-Level/Portable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crimping Force | 450 Tons | 280 Tons | 180 Tons |
| Max Hose ID | 6" Multi-Spiral | 4" 4SP/6SP | 2" 2SN/R2 |
| Automation Level | Fully Automatic (CNC, PLC) | Semi-Automatic (Digital Control) | Manual/Basic Electric (Dial Adjust) |
| Control System | Touchscreen HMI, Data Logging, IoT Ready | Digital Readout, Foot Pedal Control | Micrometer Dial, Push Button |
| Die Change System | Automatic/Quick-Change Carousel | Rack-mounted, Manual Insert | Simple Push-Out Pin |
| Key Certifications | CE, ISO 9001, TÜV | CE, ISO 9001 | CE |
| Warranty | 2-3 Years, Extended Options | 1 Year Standard | 6 Months - 1 Year |
| Typical Price Range | $30,000 - $100,000+ | $10,000 - $30,000 | $3,000 - $10,000 |
When evaluating a hose crimper for sale, factors beyond initial cost, such as long-term reliability, maintenance requirements, and the availability of local technical support, should be carefully considered to ensure the investment aligns with operational goals and budget. Vendor A exemplifies premium industrial solutions, Vendor B offers a balanced approach for many workshops, and Vendor C caters to smaller operations or field service needs.
Customized Solutions in Hose Crimping
While standard hose crimper models meet a wide range of industrial needs, specialized applications often require customized solutions. Manufacturers committed to innovation offer tailored equipment designed to address unique challenges and integrate seamlessly into existing production lines.
- Application-Specific Die Sets: For non-standard hose dimensions, proprietary fittings, or delicate hose materials, custom-machined dies can be engineered. These ensure the exact crimp profile and diameter, preserving hose integrity and maximizing sealing performance.
- Adjusted Crimping Force and Speed: Some applications require either extremely high forces for large, multi-spiral hoses or very delicate control for sensitive components. Custom hydraulic power units and control systems can be designed to deliver precise force and speed profiles.
- Integration with Production Lines: For high-volume manufacturing, crimpers can be integrated into automated assembly lines with conveyors, pick-and-place robots, and centralized control systems. This often involves custom PLC programming and communication interfaces.
- Specialized Environmental Adaptations: For operations in extreme conditions (e.g., cleanrooms, corrosive atmospheres, hazardous locations), machines can be built with stainless steel components, explosion-proof electrical enclosures, or specific contamination control features.
- Ergonomic and Safety Enhancements: Custom designs can optimize operator comfort and safety through features like adjustable workbenches, automated loading mechanisms, enhanced lighting, or specialized safety interlocks to meet particular facility regulations.
- Software Customization: For advanced data tracking, integration with ERP systems, or unique quality control protocols, custom software modules can be developed. This allows for bespoke reporting, traceability, and process optimization.
Engaging with a manufacturer that possesses strong engineering capabilities and a flexible production approach is essential for successful customized hose crimper solutions. These tailored machines not only solve specific operational challenges but also often lead to significant improvements in efficiency and product quality.
Application Case Studies: Real-World Impact
Real-world application case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of deploying high-quality hose crimper technology in challenging industrial environments. These examples highlight enhanced operational safety, reduced downtime, and improved production efficiency.
Case Study 1: Heavy Equipment Manufacturer
- Challenge: A leading manufacturer of large excavators faced frequent hydraulic hose failures in the field, leading to costly warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction. Their existing crimping equipment lacked the precision and consistency required for high-pressure, large-diameter hose assemblies.
- Solution: They invested in a state-of-the-art hyd hose crimper with a 450-ton crimping force and digital control for crimp diameter accuracy within ±0.05mm. The new machine included a quick-change die system and data logging capabilities.
- Results: Over 12 months, the field failure rate for hydraulic hoses decreased by 65%. Warranty costs related to hose assemblies dropped by 40%, and customer satisfaction scores improved. The enhanced precision ensured compliance with ISO 6803 and SAE J517 standards for hydraulic hose assemblies, reinforcing product quality and reliability.
Case Study 2: Petrochemical Plant Maintenance
- Challenge: A large petrochemical complex required frequent on-site replacement and repair of industrial hoses for chemical transfer, steam lines, and cooling systems. The remote locations and need for rapid, safe repairs made transport of assemblies cumbersome and often delayed critical operations.
- Solution: The plant procured several heavy-duty, yet portable, electric hose crimper units, rated for up to 3" multi-spiral hoses, which could be easily transported to various sections of the facility. These units were equipped with explosion-proof motors and digital controls for consistent crimping.
- Results: On-site repair times were reduced by an average of 70%, significantly minimizing operational downtime. The precise crimping capabilities ensured that all new hose assemblies met stringent API 1529 standards for hydrocarbon transfer hoses, enhancing worker safety and environmental protection by preventing leaks.
Case Study 3: Agricultural Equipment OEM
- Challenge: An OEM producing agricultural machinery needed to streamline their hose assembly production line. Manual crimping processes were slow and prone to inconsistencies, creating bottlenecks and affecting overall throughput.
- Solution: The OEM implemented an automated hose crimper with integrated loading and unloading features, capable of handling a variety of hose sizes from 1/4" to 2". The system was integrated with their existing inventory management software for real-time tracking of crimp data and material consumption.
- Results: Production efficiency for hose assemblies improved by 120%, eliminating the previous bottleneck. Crimp quality consistency reached near 100%, reducing scrap rates and enhancing the overall reliability of their agricultural machinery. The automated system also reduced labor costs by 25% in the hose assembly department.
Trustworthiness: FAQ, Lead Time, Warranty & Support
Building trust with B2B clients requires transparency in product information, operational logistics, and post-purchase support. This section addresses common inquiries and commitments from reputable hose crimper manufacturers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Q1: How do I determine the correct crimp diameter for my hose and fitting?
A1: Reputable manufacturers provide detailed crimp specifications (e.g., crimp charts) for their hoses and fittings. These charts specify the target crimp diameter, which is crucial for achieving a secure, leak-free connection. Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations or utilize digital crimpers with built-in databases.
Q2: What maintenance is required for a hydraulic hose crimper?
A2: Regular maintenance includes checking hydraulic fluid levels and quality (typically every 500-1000 hours), lubricating die segments and the crimping head (daily/weekly), inspecting electrical connections, and cleaning the machine. Following the manufacturer's specific maintenance schedule is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Q3: Can a single crimper handle different types of hoses and fittings?
A3: Yes, most modern industrial crimpers are highly versatile. They use interchangeable die sets to accommodate various hose diameters and fitting configurations (e.g., straight, elbow, banjo). Always ensure the machine's maximum crimping force and die opening are sufficient for your largest hose and fitting combinations.
Lead Time and Fulfillment:
Standard hose crimper models are typically available with lead times ranging from 4-8 weeks, depending on inventory levels and customization requirements. For specialized or custom-engineered solutions, lead times may extend to 12-16 weeks. Expedited shipping options are often available upon request, and robust logistics networks ensure global delivery.
Warranty Commitments:
Most reputable manufacturers offer a standard warranty of 1 to 2 years on parts and workmanship for their hose crimper machines. Extended warranty options are often available, providing additional peace of mind and protection for your investment. This typically covers manufacturing defects and component failures under normal operating conditions.
Customer Support and After-Sales Service:
Comprehensive customer support is critical for industrial equipment. This includes:
- Technical Assistance: Access to skilled technicians via phone, email, or online portal for troubleshooting and operational guidance.
- On-site Service: Availability of field service engineers for installations, preventative maintenance, and complex repairs.
- Spare Parts Availability: A readily accessible inventory of critical spare parts to minimize downtime.
- Training Programs: Offering training for operators and maintenance staff to ensure safe and efficient use of the equipment.

Conclusion
The hose crimper stands as a cornerstone technology in modern industrial infrastructure, directly influencing the safety, efficiency, and reliability of fluid power systems across virtually every sector. From the meticulous engineering and material selection during manufacturing to the integration of advanced digital controls and IoT capabilities, these machines are continuously evolving to meet increasingly stringent performance demands. The careful consideration of technical specifications, application-specific needs, and robust vendor support is paramount for B2B decision-makers. Investing in a high-quality, precisely engineered hose crimper is not merely a purchase; it is a strategic decision that underpins operational resilience, reduces costly downtime, and ultimately contributes to the long-term success and safety of industrial enterprises.
References:
- ISO 9001:2015 - Quality management systems - Requirements. International Organization for Standardization.
- SAE J517 - Hydraulic Hose. SAE International.
- ANSI B30.1 - Jacks, Industrial Rollers, Air Skates, and Caster-Type Dollies. American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
- API 1529 - Flexible Pipe and Hose for Marine Loading and Unloading Operations. American Petroleum Institute.
- Parker Hannifin Corporation. (2023). Hose Products Division Reference Guide.
-
Top Hose Crimper Sales: Hydraulic, Manual & Electric OptionsNewsAug.28,2025
-
Precision Belling Machine | Automated Pipe End FormingNewsAug.27,2025
-
High-Efficiency Automatic Belling Machine for PipesNewsAug.26,2025
-
High-Quality Line Pipe Steel for Oil & Gas PipelinesNewsAug.21,2025
-
Advanced PVC Belling Machine for Efficient Pipe ProductionNewsAug.19,2025


