Feb . 19, 2025 07:43
Back to list
3d roll forming
In the world of materials processing, the two roll mill stands as an indispensable tool for transforming various polymers and elastomers into manageable, homogeneous compounds. Its impressive track record spans multiple industries, showcasing a blend of engineering expertise and materials science prowess. For those looking to delve into the intricacies of the two roll mill's capabilities, it's essential to understand its operational nuances and myriad benefits.
Safety remains a paramount concern when working with such powerful machinery. Two roll mills are equipped with an array of safety features, including emergency stop buttons and protective bars, designed to mitigate risks. Operators are trained extensively to recognize potential hazards, ensuring that processes adhere to strict safety protocols. This commitment to safety builds trust—both within teams and with clients—reinforcing the machine's place as a reliable component of industrial production lines. From an authoritative standpoint, the utility and effectiveness of two roll mills are backed by decades of industrial usage and academic research. Their role in facilitating innovation in material science cannot be overstated, as they enable the creation of new materials with enhanced properties. As advances in polymer science evolve, so too do the capabilities of the two roll mills, adapting to ever-changing industrial needs. In conclusion, two roll mills are not just machines; they are an embodiment of advanced scientific principles combined with practical engineering design. Their enduring presence in the industry is a testament to their effectiveness, adaptability, and the depth of expertise required to operate them. As industries continue to innovate, the two roll mill will undoubtedly remain a vital instrument in the toolbox of efficient, cutting-edge material processing.
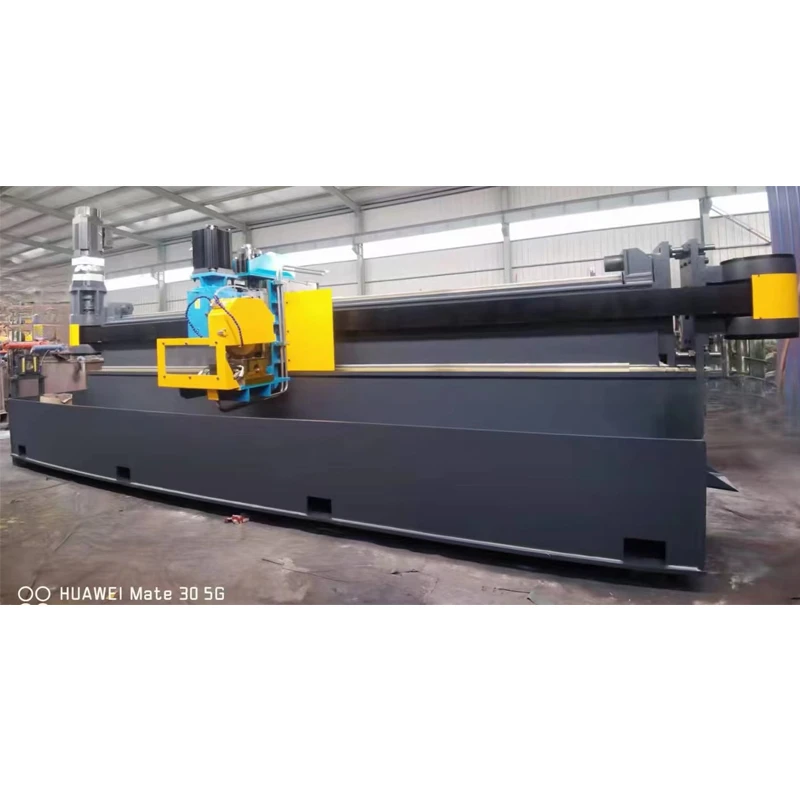
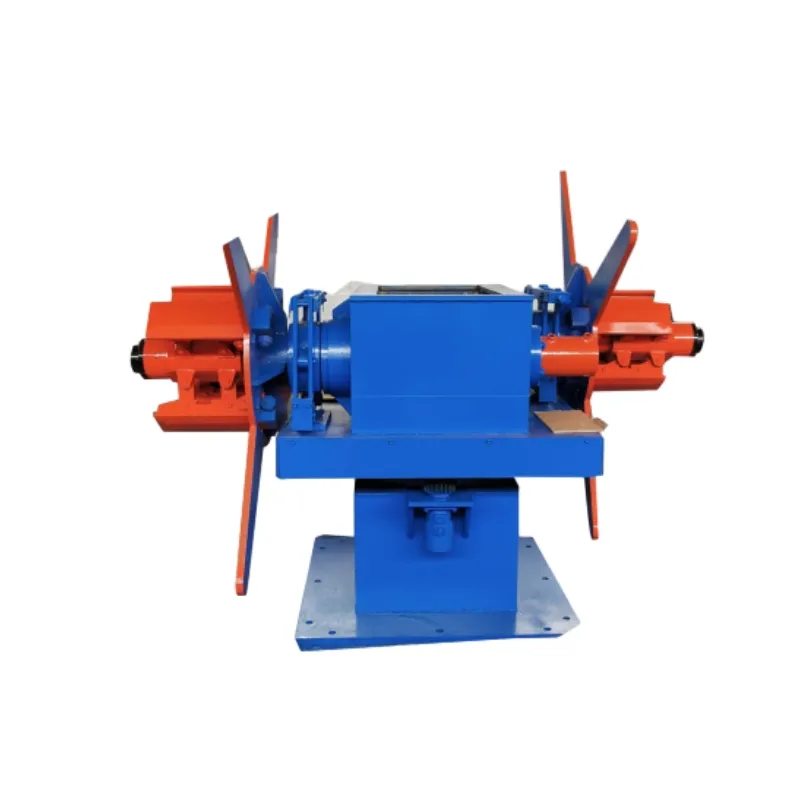

Safety remains a paramount concern when working with such powerful machinery. Two roll mills are equipped with an array of safety features, including emergency stop buttons and protective bars, designed to mitigate risks. Operators are trained extensively to recognize potential hazards, ensuring that processes adhere to strict safety protocols. This commitment to safety builds trust—both within teams and with clients—reinforcing the machine's place as a reliable component of industrial production lines. From an authoritative standpoint, the utility and effectiveness of two roll mills are backed by decades of industrial usage and academic research. Their role in facilitating innovation in material science cannot be overstated, as they enable the creation of new materials with enhanced properties. As advances in polymer science evolve, so too do the capabilities of the two roll mills, adapting to ever-changing industrial needs. In conclusion, two roll mills are not just machines; they are an embodiment of advanced scientific principles combined with practical engineering design. Their enduring presence in the industry is a testament to their effectiveness, adaptability, and the depth of expertise required to operate them. As industries continue to innovate, the two roll mill will undoubtedly remain a vital instrument in the toolbox of efficient, cutting-edge material processing.
Prev:
Next:
Latest news
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line-BzZhou Xinghua Machinery Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTD.|line pipe steel&welded gas pipeNewsJul.30,2025
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line-BzZhou Xinghua Machinery Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTD.|High Precision&Automated SolutionsNewsJul.30,2025
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line - BzZhou Xinghua Machinery Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd.NewsJul.30,2025
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line-BzZhou Xinghua Machinery Equipment Manufacturing Co., LTD.|Precision Welding, High EfficiencyNewsJul.30,2025
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line|BzZhou Xinghua|Precision Welding&EfficiencyNewsJul.30,2025
-
High Frequency Straight Seam Welded Pipe Production Line - BzZhou Xinghua|Precision Engineering&EfficiencyNewsJul.30,2025


